
WebElements Periodic Table » Iron » properties of free atoms
This activity checks on the misconceptions that: The structure of iron is an example of a giant molecule. The atoms of iron are held together by ionic bonds. Iron conducts electricity because iron atoms move through the solid. Iron expands when heated because the atoms get bigger. Iron metal is silver because iron atoms are silver.

Iron Facts Atomic Number 26 or Fe
Name: Iron Symbol: Fe Atomic Number: 26 Atomic Mass: 55.845 amu Melting Point: 1535.0 °C (1808.15 K, 2795.0 °F) Boiling Point: 2750.0 °C (3023.15 K, 4982.0 °F) Number of Protons/Electrons: 26 Number of Neutrons: 30 Classification: Transition Metal Crystal Structure: Cubic Density @ 293 K: 7.86 g/cm 3 Color: Silvery Atomic Structure

Periodic Network 2012 [licensed for use only] / Iron
Iron -. Fe: properties of free atoms. Iron atoms have 26 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.14.2. The ground state electron configuration of ground state gaseous neutral iron is [ Ar ]. 3d6. 4s2 and the term symbol is 5D4.
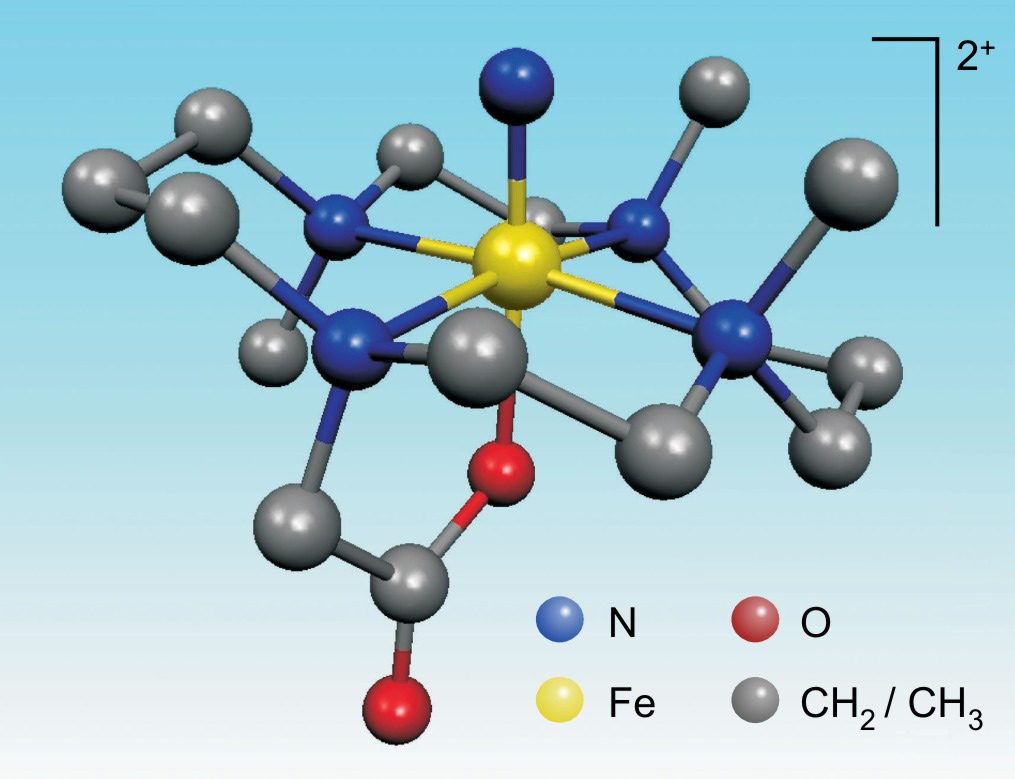
caption a rendering of the molecular structure of a new species of iron iron vi the new form of iron
Abstract The integration of highly active single atoms (SAs) and atom clusters (ACs) into an electrocatalyst is critically important for high-efficiency two-electron oxygen reduction reaction (2e- ORR) to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).

Iron, atomic structure Stock Image C018/3707 Science Photo Library
In the body-centered cubic structure, each atom forms a total of 14 bonds to neighboring atoms, although six of these bonds are somewhat weaker than the other eight.. Below 910C, iron metal packs in a body-centered cubic structure, in which the holes are too small to hold carbon atoms.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Iron-58b602243df78cdcd83d3d5a.jpg)
Atoms Diagrams Electron Configurations of Elements
Fig. 1. Melting temperature TM, and density, ρ, versus atomic number Z of the elements of the first transition period. Iron is found between these two groups of elements. It crystallizes in both the fcc (912° < Tγ < 1394°C) and the bcc lattices (1394° > Tα < 1538°C) and again at Tα <912°C.

Flashcard of iron with atomic mass Royalty Free Vector Image
A neutral iron atom contains 26 protons and 30 neutrons plus 26 electrons in four different shells around the nucleus. As with other transition metals, a variable number of electrons from iron's two outermost shells are available to combine with other elements.

Iron, atomic structure Stock Image C023/2516 Science Photo Library
Structure, properties, spectra, suppliers and links for: Iron, 7439-89-6, 8048-10-0, 33485-98-2, 70892-58-9. Jump to main content Jump to site nav. Home;. An elemental iron in which the atom has an oxidation state of zero. ChEBI CHEBI:18248, CHEBI:82664: An iron group element atom that has atomic number 26. ChEBI CHEBI:18248,.

Iron Atomic Structure
Learn More About Dino Light & Find An Authorized Dino-Lite Reseller Today!

Iron, atomic structure Stock Image C045/6366 Science Photo Library
The Fe atom labeled with S as the core of the cluster essentially break away from the coordination relationship within 0.5 ps. Therefore, it can be inferred that S does not establish a stable binding force with Fe atom within the iron-based melt. S atoms exist among numerous Fe atoms, occupying considerable space in between.
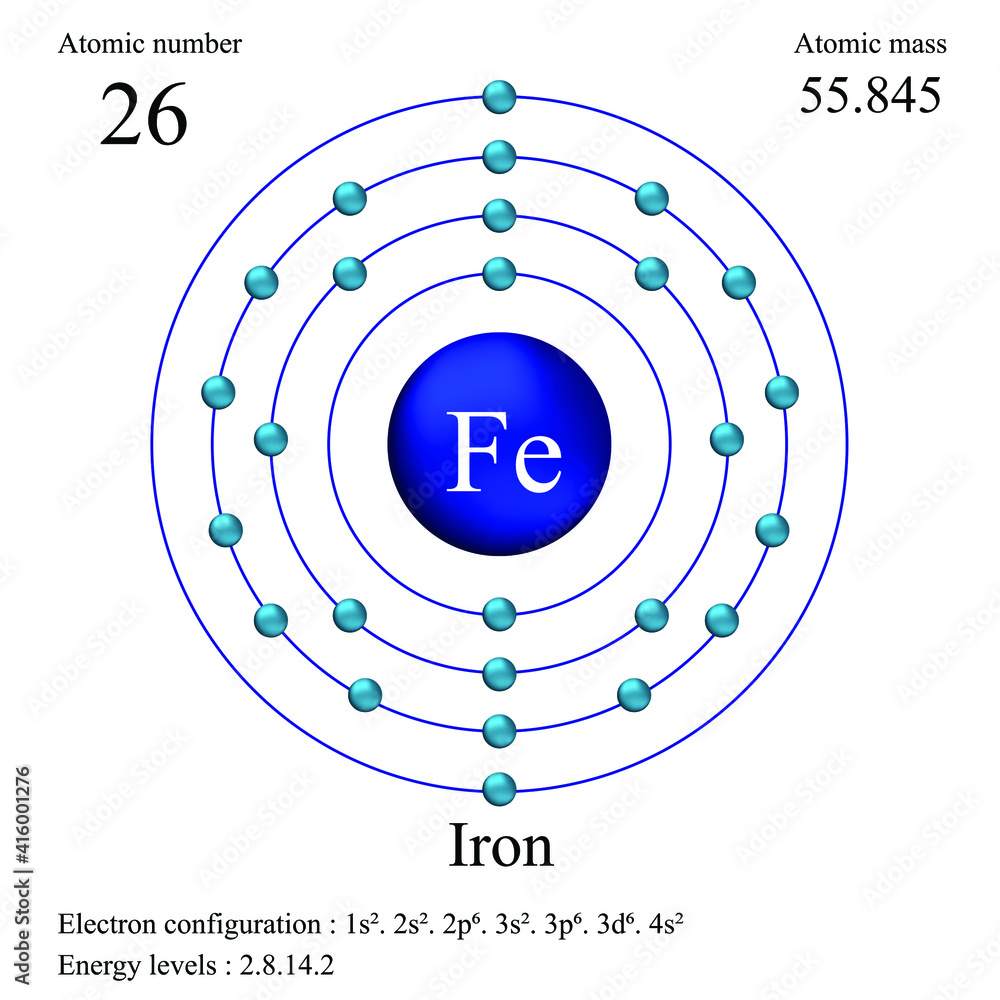
Iron atomic structure has atomic number, atomic mass, electron configuration and energy levels
Crystal structure: cubic, body centered: Physical properties; State of matter. A typical iron atom has 56 times the mass of a typical hydrogen atom. Iron is the most abundant metal, and is believed to be the tenth most abundant element, in the universe.

Bohr Model Iron Atom Electron Structure Stock Vector (Royalty Free) 1951417030 Shutterstock
Iron has two different crystal structures at atmospheric pressure: the body centered cubic (bcc) and the face centered cubic (fcc). In the ground state the bcc α-phase is stable, and at the temperature T=1184 K (A 3 point), α-Fe transforms into fcc α-Fe, which is stable up to 1665 K (A 4 point). Above this temperature, iron transforms back.

Iron Protons Neutrons Electrons Electron Configuration
Characteristics Allotropes Molar volume vs. pressure for α iron at room temperature At least four allotropes of iron (differing atom arrangements in the solid) are known, conventionally denoted α, γ, δ, and ε . The first three forms are observed at ordinary pressures.

Iron, atomic structure Stock Image C013/1539 Science Photo Library
Iron is also the fourth most common element in Earth's crust by weight and much of Earth's core is thought to be composed of iron.. Atomic weight (average mass of the atom): 55.845; Density: 7..

Iron atom Bohr model stock vector. Illustration of isolated 267662069
This iron atom has 26 protons and 56 − 26 = 30 neutrons. Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\) How many protons are in \(\ce{_{11}^{23} Na}\). The Bohr model of the atom was the first complete physical model of the atom. It described the overall structure of the atom and how atoms bond to each other. Bohr's planetary atomi model was not perfect and.
Symbol and electron diagram for Iron illustration Stock Vector Image & Art Alamy
Element Iron (Fe), Group 8, Atomic Number 26, d-block, Mass 55.845. Sources, facts, uses, scarcity (SRI), podcasts, alchemical symbols, videos and images.. The mass of an atom relative to that of carbon-12. This is approximately the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.. These atoms that have been lost from the.